Dka Criteria Uptodate

Uptodate electronic clinical resource tool for physicians and patients that provides information on adult primary care and internal medicine allergy and immunology cardiovascular medicine emergency medicine endocrinology and diabetes family medicine gastroenterology and hepatology hematology infectious diseases nephrology and.
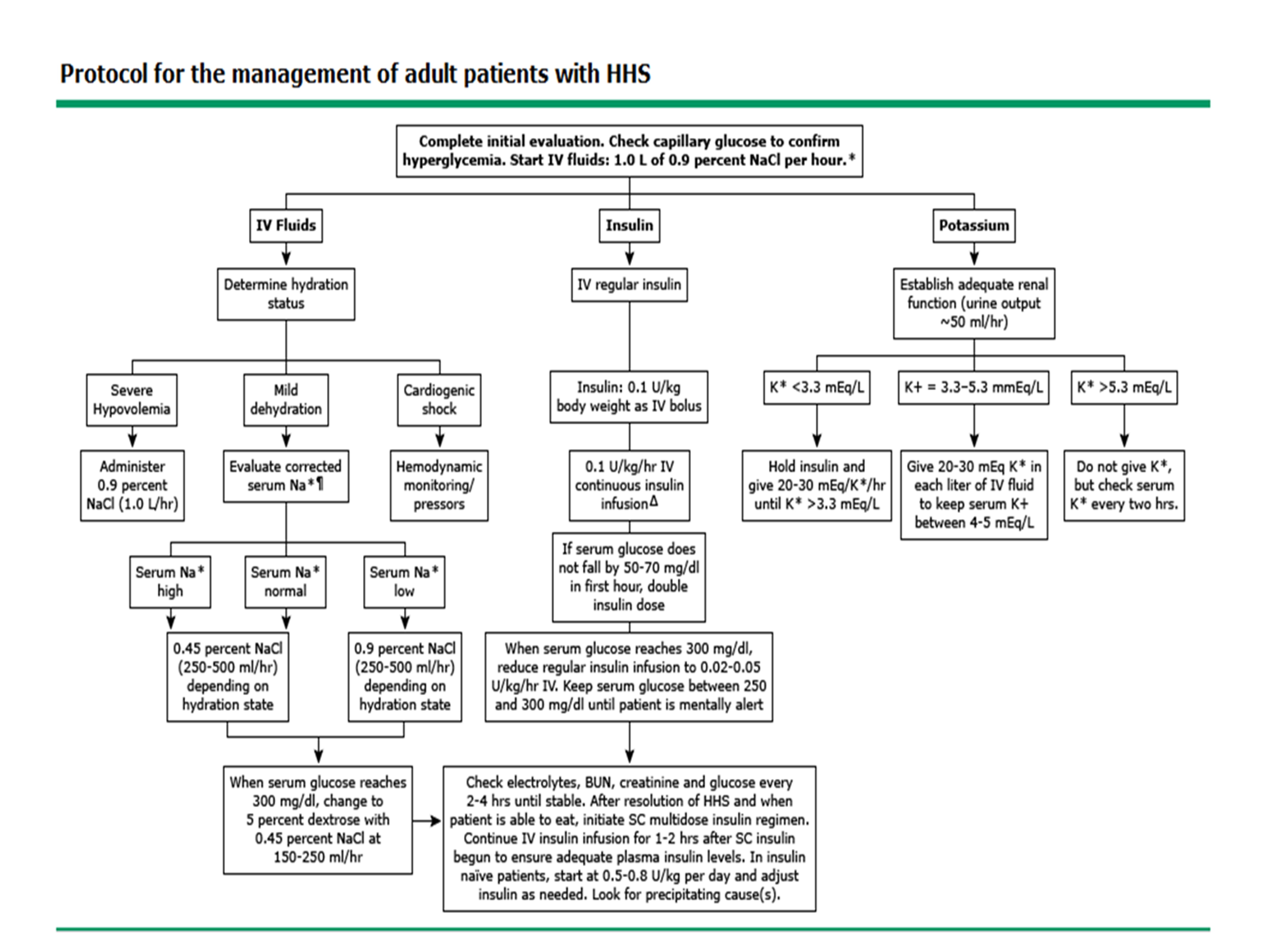
Dka criteria uptodate. Diabetic ketoacidosis dka is characteristically associated with type 1 diabetes. 1 the biochemical criteria for the diagnosis of dka are hyperglycemia blood glucose level 200 mg dl 11 1 mmol l venous ph less than 7 3 or serum bicarbonate level less than 15 meq l 15 mmol l and ketonemia blood β hydroxybutyrate concentration 3 mmol l or moderate or severe ketonuria. Hyperglycemia blood glucose of 200 mg dl 11 mmol l. Diabetic ketoacidosis dka and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state hhs also known as hyperosmotic hyperglycemic nonketotic state hhnk are two of the most serious acute complications of diabetes.
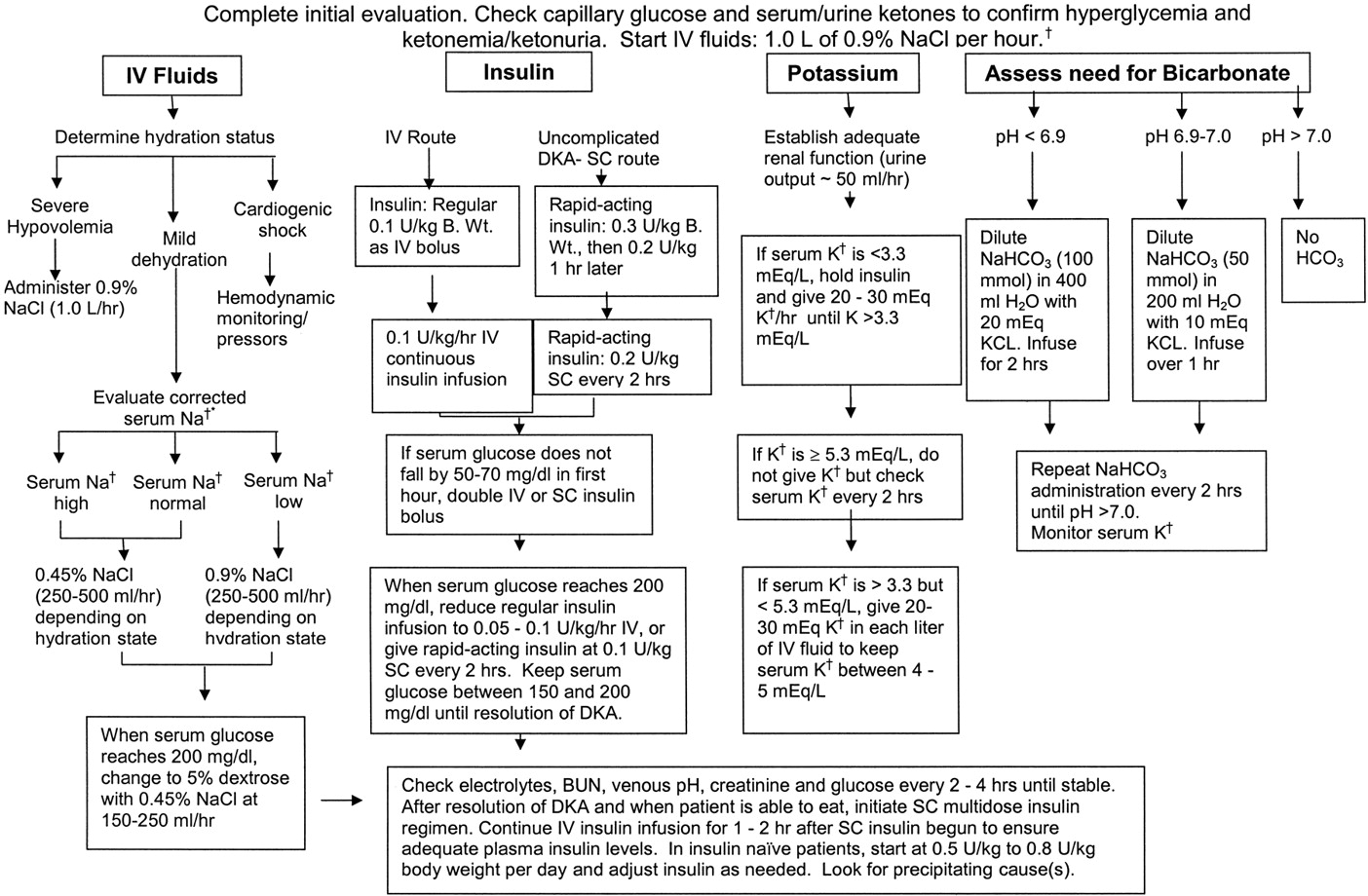
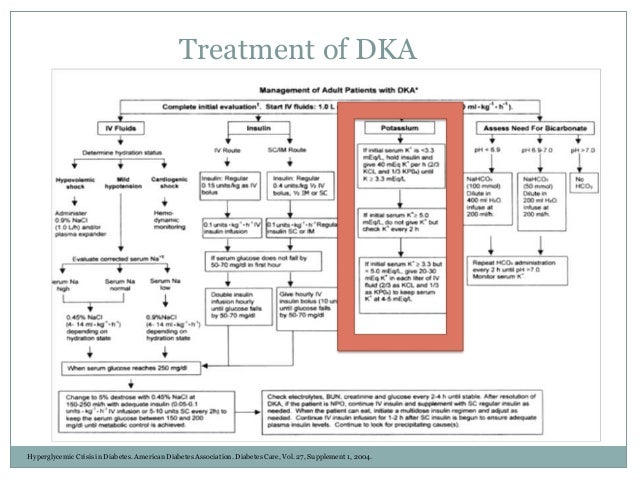
Diabetic ketoacidosis diabetic ketoacidosis dka is defined by the presence of all of the following in a patient with diabetes as outlined in a consensus statement from the international society for pediatric and adolescent diabetes ispad in 2018 9. Diabetic ketoacidosis dka critical care guideline two bag system. Requires critical care level of care. It occurs at the time of diagnosis of type 1 diabetes in approximately one third of children in the united states in children with established diabetes dka occurs at rates of 6 to 8 percent per year dka can also occur in children with type 2 diabetes.
Dka is characterized by ketoacidosis and hyperglycemia while hhs usually has more severe hyperglycemia but no ketoacidosis table 1. Configctrl2 info metadescription devastating consequence of diabetic ketoacidosis dka this complication is far more common among children with dka than among adults. It also occurs in type 2 diabetes under conditions of extreme stress such as serious infection trauma cardiovascular or other emergencies and less often as a presenting manifestation of type 2 diabetes a disorder called ketosis prone diabetes mellitus. Diabetic ketoacidosis dka is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
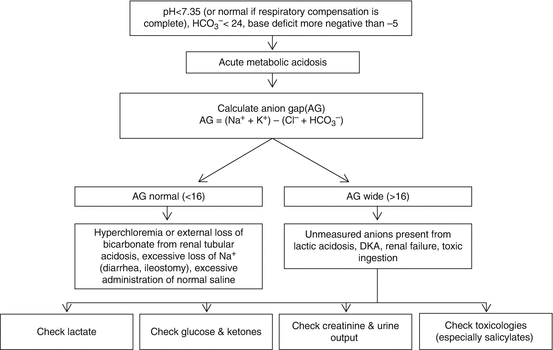
Children presenting with more severe dka higher blood urea nitrogen. Metabolic acidosis was confirmed with a ph of 7 3 bicarbonate concentration of 10 meq l and an elevated anion gap of 29 meq l sodium 134 meq l potassium 5 7 meq l chloride 101 meq l b continue reading.