Dka Pathophysiology Nursing

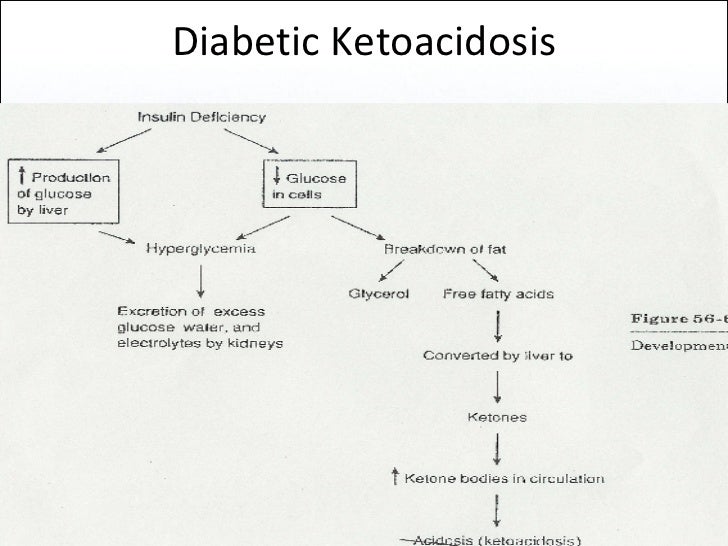
When this happens the body begins to break down fat as energy which produces a build up of acid in the bloodstream called ketones.
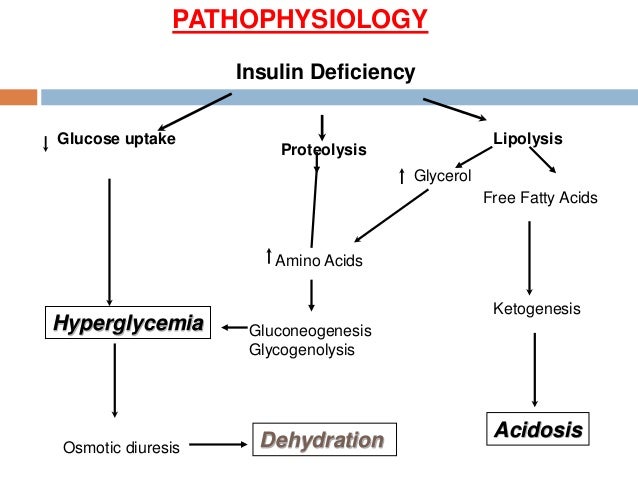
Dka pathophysiology nursing. Physical examination findings such as hypotension tachycardia poor skin turgor and weakness support the clinical diagnosis of dehydration in dka. This occurs because the blood sugar is so elevated and there is not enough insulin to take the sugar to the cell. In this video we ll break down dka pathophysiology so that you can finally understand it for nursing school. Diabetic ketoacidosis also known as dka is one of those harder topics to learn in nursing school.
Signs symptoms include polyuria polydipsia hyperglycemia greater than 300 mg dl kussmaul breathing acetone breath. The fluids you give to your patient will depend on their particular situation and what the doctor has ordered but they may include normal saline lactated ringers 0 45 nacl or d5 1 2ns. The cell needs energy. Pathophysiology diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes mellitus that occurs when uncontrolled blood sugar rises and the body can t produce enough insulin to use the glucose.
There are 3 main nursing interventions for dka. Dka management includes controlling hyperglycemia ketosis and acdidosis. Pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis diabetic ketoacidosis is one of the potentially life threatening acute complications of diabetes mellitus. Diabetic ketoacidosis dka occurs with severe hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis.
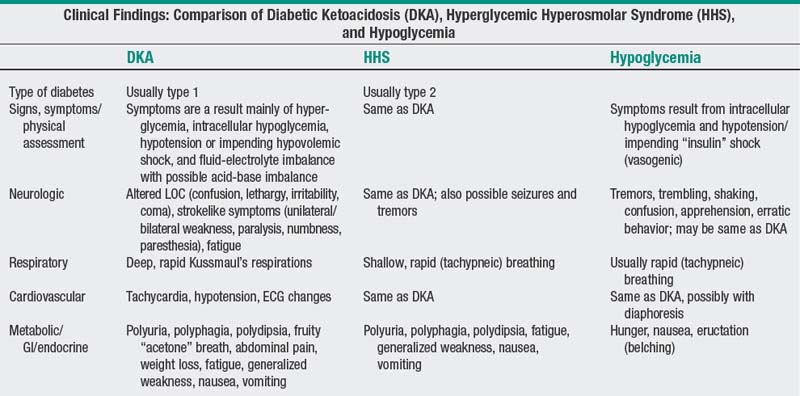
Polyuria polydipsia weight loss vomiting and abdominal pain usually are present in patients with dka. Fluids insulin and of course continuing to assess your patient. It is important to know the differences between diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome hhns because the two complications affect the diabetic patient. Complications of diabetic ketoacidosis throughout the age spectrum and during pregnancy require a close evaluation of symptoms testing treatment and outcomes to treatment.
Diabetic ketoacidosis dka is a serious and potentially life threatening complication of diabetes joint british diabetes societies 2013. In the past diabetic ketoacidosis was considered as the hallmark of type i diabetes but current data show that it can be also diagnosed in patients with type ii diabetes mellitus. It is a complex disordered metabolic state characterised by hyperglycaemia elevated blood glucose acidosis ph imbalance and ketonaemia excess ketones in the blood. And all of these can be tricky to learn as a nursing student.
Abdominal pain can be closely associated with acidosis and resolves with treatment. However there are subtle difference between the two conditions. Don t forget to take the dka quiz. Dka is a life threatening condition of diabetes mellitus.